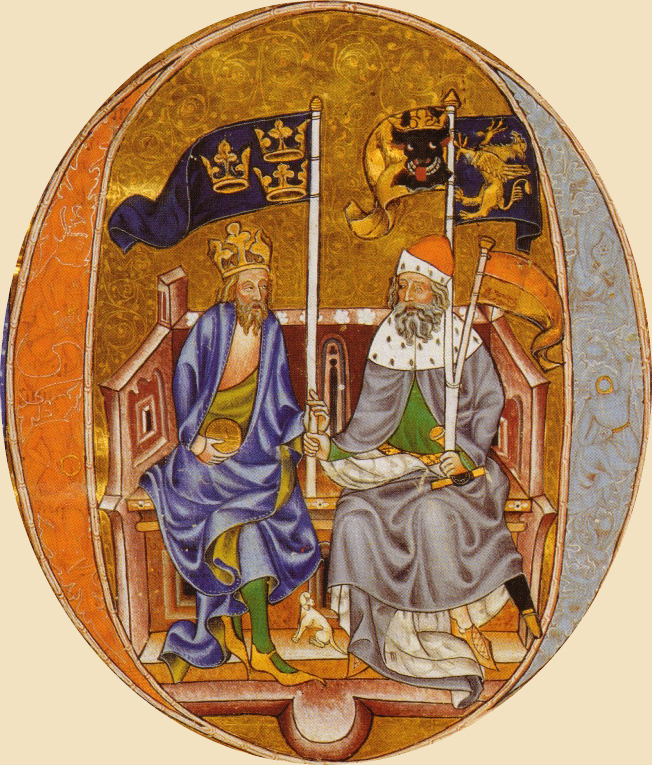
Long live the king
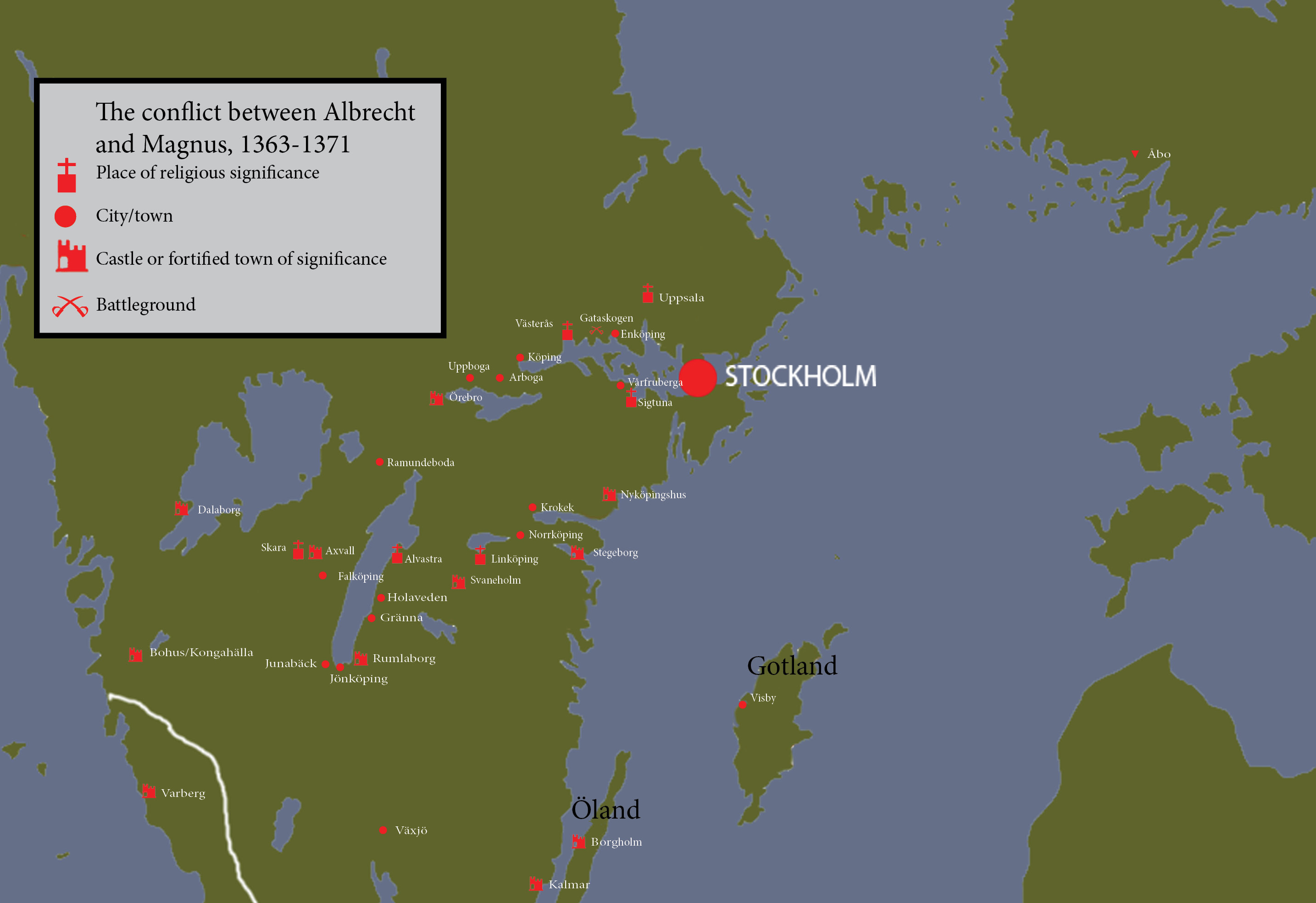
The war against Magnus Eriksson had been an expensive one. Magnus had acted decisively when Albrecht went to Åbo to continue the siege after his marsk (marshal/military commander) Nils Turesson was killed in 1364. As mentioned, Magnus’ actions culminated in the battle of Gataskogen, where he was captured. At the opposing side were German knights, for example the mentioned Henrik van Ouwen, Rawen van Barnekow and Vicke van Vitzen. They expected compensation and rewards for their loyalty, but the Swedish coffers were appallingly empty and Albrecht had to find another way to pay off his countrymen. His solution was to grant the foreging knights land. During his first year as a king the young king was forced to pawn more than half of his kingdom. The Swedish nobles were outraged, which is easy to understand; if the king pawned land to Germans, there wasn’t much land left for them.
Furthermore, the Germans tended to see the Swedish commoners as little more than resources to be exploited. The Swedish model with a free, armed peasant class with extensive rights wasn’t at all what the Germans were used to, so they merely scoffed at the commoners’ claims. A chronicler described them as ”birds of prey” and it was generally agreed that the new masters ruled against tradition and law. In Sweden it was formally peace, as the old king Magnus had recognized Albrecht as king. This meant that nobody needed German and Danish mercenaries, which as a result became unemployed. In the following years the unemployed soldiers drifted through the lands, pillaging and stealing.
An old verse tells the tale of the relentless robbers
Jak wil idher tydha aff then rääff
som wäl weet badhe hool oc grääff
ther menar iak mz then legodräng
som haffuer fordarffuat badhe aker oc äng
the wilia alla til hoffua rijda
widh bondans kornladu at strijda
fik han eena kogerbysso oc pijla vti
tha skulle iw bonden til skogen fly
spangat bälte oc krusat haar
rostad swärd oc staalhandske widh hans laar
rijdher i gardh oc gar i stuffua
sidhan wil han fatiga bondan truffua
hustru huar är tin vnga höna
then skal tu ey länger for mik löna
ligger hon sik i bänk eller pall
bär henne fram oc äggen all
hon sitter ey sa högt a rang
iak slar henne nider mz min spiwtz stang
haffuer tu ey meer än ena gaas
then skulom wij i apton haffua til kraas
han beder uptända fempton lius
han drykker oc skrölar i fullan duus
thz monde the edela bönder söria
at legodrängar skola tolkin leek vpböriaI would like to tell you about the fox
That well know both hole and ditch
I mean by this the mercenary
Who has destroyed both field and meadow
They will all happily ride
By the farmer’s larder to fight
If he had a quivergun with arrows
The farmer would flee to the forests
Belt with metal plaques and curled hair
Rusty sword and a steel gauntlet by his thigh
He rides to the farms and goes in the house
Then he likes to force the poor peasant
Wife, where is your young hen
You should not hide it from me anymore
If she lies under bench or stool
Bring her to me along with her eggs
If she sits high on her perch
I will strike her down with my spear
Have you not more than a single goose
Tonight we’ll have it for a meal
He says to light fifteen candles
He drinks a shouts and feasts
That the noble peasants may mourn
That mercenaries should start such a game
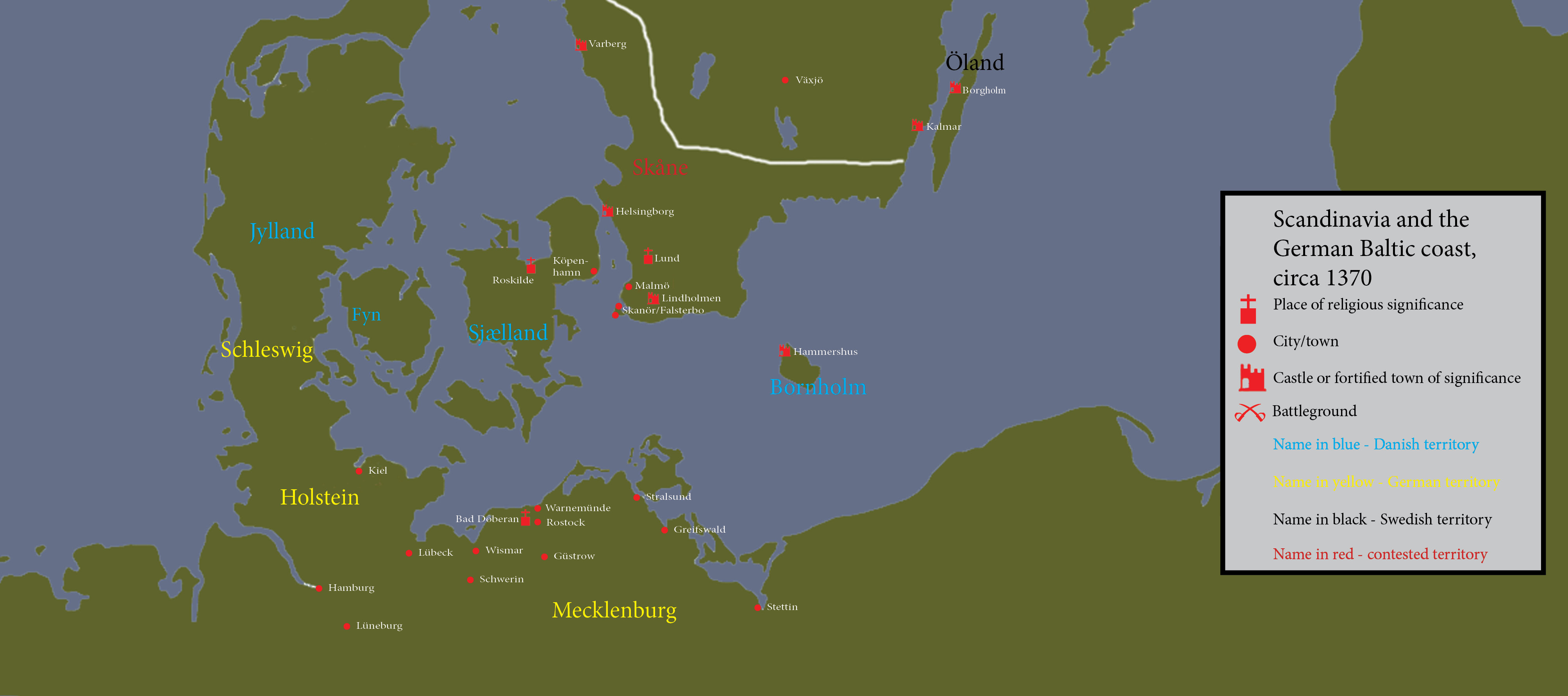
This was, of course, a rebellion waiting to happen. But Albrecht was in no way out of the game. 1375 the old Danish king Valdemar Atterdag died, which meant that king Albrecht’s family could have a real shot at the Danish throne. Atterdag’s son Kristoffer was killed in 1363, which meant that the son of his oldest daughter Ingeborg was next in line. The good thing about this was that Ingeborg was married to duke Heinrich of Mecklenburg, king Albrecht’s older brother. Furthermore, Valdemar had signed a treaty with the Mecklenburgers in 1371, where he promised that the grandson in question should inherit the crown. Everything seemed to go Albrecht’s way – if his nephew, also an Albrecht, could be put on the throne of Denmark he would not only be rid of an enemy – he would also gain a powerful and rich ally.
There was only one problem. The treaty with the Mecklenburgers was never ratified by the Danish council. Instead the Danish nobles referred to an earlier, and ratified, agreement with the Hansa, where it was stated that the Hanseatic cities had a say when it came to which king that would rule Denmark if Valdemar should perish.
Enter Margareta
The Danish nobles turned to Margareta, the younger sister of Ingeborg. She had a son with Håkan of Norway, and because of Norwegian law he had already inherited the throne after his father. His name was Olof, and it was on him that the Danish highborns put their money. The conflict was a fact. The Mecklenburgers and the Holsteiners make an alliance to put young Albrecht on the Danish throne. They are lead by the old duke Albrecht of Mecklenburg – king Albrecht’s father, and invade Skåne in the end of the 1370’s. However, they achieve very little, and old Albrecht dies in the beginning of 1379. At this point king Albrecht of Sweden join the war to support young Albrecht (confused yet? It’s Albrecht VI von Mecklenburg who is in question here) in his struggle for the throne and to try and reclaim Halland and Skåne. He too achieves little, and in 1380 Danes and Norwegians burn the cities of Jönköping, Skara, Örebro and Västerås. In 1381, the war comes to a standstill and eventually it is discontinued. This, in effect, meant that the young Olof was elected king even in Denmark. As he was a minor, his mother ruled in his place, something that probably suited her quite well.
The mightiest man in Sweden
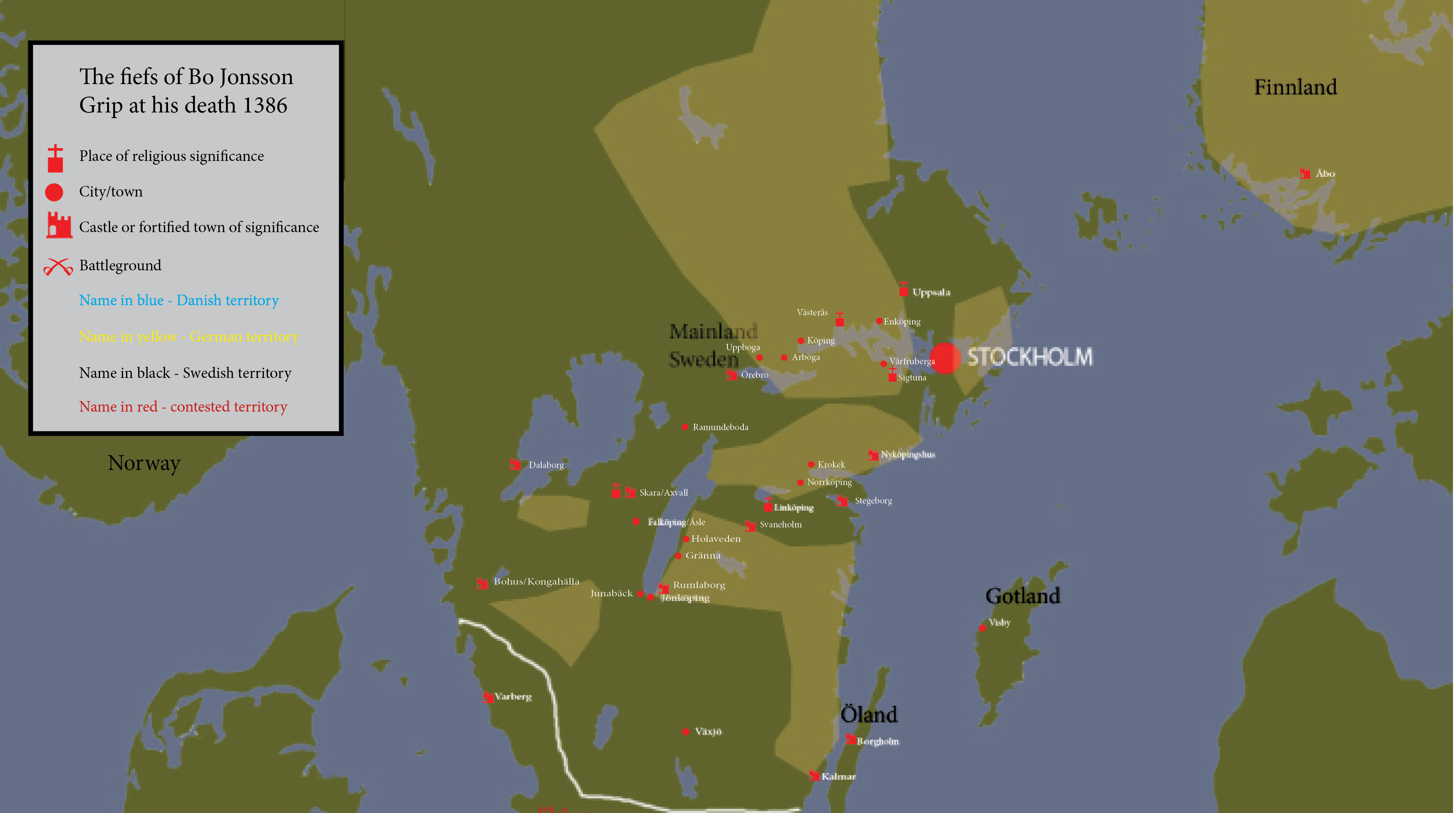
Albrecht may have been king, but in fact, he ruled very little of Sweden. Bo Jonsson Grip, the king’s drots (which meant he was the second in charge and also the supreme judge of Sweden) owned most parts of Sweden, including all of Finnland and the vast region of what was then called Hälsingland (now Norrland). More specifically, he owned or administered Stockholm, Nyköping, Kalmar, Viborg, Raseborg, Tavastehus, Korsholm, Öresten, Oppensten and Rumlaborg counties. But all good things must come to an end, and Bo Jonsson died in 1386. If king Albrecht could get his hands on even half of those estates, farms and castles, his fiscal problems would be over in a glimpse. He thought up a plan, and summoned the ten executors that were appointed to administer the deceased drots’ assets. None of them showed up, which was probably a wise move, but at the same time they took a stand by disobeying a direct order from the king.
But the king had another plan. He tried to force the widow of the drots, Margareta Dume, to choose him as her guardian. At the same time he wanted to reclaim lands and estates that the nobles ”unlawfully” claimed after the uprising in 1371. Last but not least he wanted to impose a special tax which would include otherwise tax-exempted lands. This was too much for the nobles, and as usual they tried to replace one master with another. They turned to Margareta and her young son Olof, king of Denmark and Norway. As Olof was a nephew of the late Magnus Eriksson (the ex-king who drowned), he was in fact entitled to compete for the Swedish throne. Ironically, it was just what the nobles feared in 1363, only now they saw it as their only chance to get rid of a hated garp (a medieval Swedish word for both a German and for someone who is a pain in the ass).
Allmighty mistress and proper master
Everything seemed to be set, and the Swedish nobility turned their hopes to the daughter of their old arch enemy, but the 3rd of Augusti 1387 Olof suddenly died from disease. It is easy to imagine that king Albrecht said his evening prayers with unusual enthusiasm when he heard the news. In theory, nothing could stop him now. Margareta was in an extremely precarious situation; her position, her power – her whole life – depended on her status as the queen mother of Olof. Now that he was dead she would quickly be swept aside. Only, she weren’t. A week after the death of her son she was elected protector of Denmark and ”allmighty mistress and proper master”. It is equally easy to imagine how king Albrecht just skipped his evening prayers when he heard those news. In february 1388 she was also elected sovereign of Norway. Her sister Ingeborg’s grandchild Bogislav of Pomerania, whom she adopted, was elected her successor.
In March 1388, one month after the election in Norway, she met the leaders of the opposition against the king at the Swedish castle Dalaborg, deep into territories that the king never really was able to master, at the western beach of lake Vänern. Most of them were part of the council; nine of the 12 members of the council were the above mentioned executors appointed by Bo Jonsson Grip. It is no exaggeration to state that those that congregated at Dalaborg were enemies of the king. They elected Margareta as allmighty mistress and proper master of Sweden, on behalf of the people and the realm.
This article was written by Peter Ahlqvist.
Read the fourth and final part here.